Objective
The objective of the performance Testing to generate traffic against a MQ system and identify, how many messages /seconds, we can send to a RabbitMQ instance also the performance Benchmarking.
Testing Approach
- RabbitMQ is an open-source message-broker software (also known as message-oriented middleware) that originally implemented the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol and these are many baseline pointers are followed to achieve performance testing goals.
- One publisher publishes as fast as it can, while one consumer consumes as fast as it can Two publishers and no consumers (performance as the queue gets longer)
- One consumer consumes a long queue from the previous test (performance of consumers unaffected by publishers)
- One consumer consumes a long queue from the previous test (performance of consumers unaffected by publishers)
- Five queues, each has 1 publisher publishing at 10k messages/s and 1 consumer (the total expected throughput is 50k/s, we look at the latency)
- Fanout to 10 queues – 1 publishers and 10 consumers, a fanout exchange
- One publisher, one consumer, but only 1 unconfirmed message (the publisher waits for the confirmation of the previous message before sending the next one)
- Fan-in: 7000 publishers publishing 1 message per second, to a single queue
- 1000 publishers publish 10 messages/s, each to a different queue; each queue has a consumer as well (total expected throughput: 10k/s
Performance Matrices:
JMeter Matrices
- 90% Average Response Time
- Throughput
- Error Percentage
- Request per Second
- API Errors
Hardware Matrix
- CPU stats (user, system, iowait & idle percentages)
- Memory usage (used, buffered, cached & free percentages)
- Virtual Memory statistics (dirty page flushes, writeback volume)
- Disk I/O (operations & amount of data transferred per unit time, time to service
- operations)
- Free disk space on the mount used for the node data directory.
- File descriptors used by beam.smp vs. max system limit.
- TCP connections by state (ESTABLISHED, CLOSE_WAIT, TIME_WAIT)
- Network throughput (bytes received, bytes sent) & maximum network throughput.
- Network latency (between all RabbitMQ nodes in a cluster as well as to/from
- Clients)
Database Matrices
- High Response Query
- Block Query
- Missing Indexes
- InnoDB Buffer Pool Size
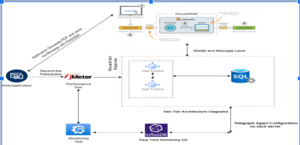
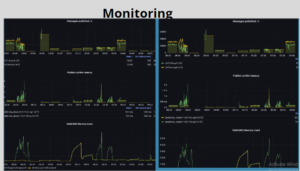
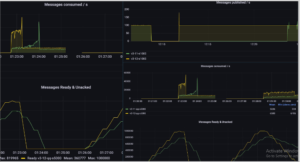

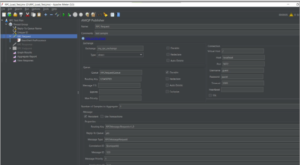
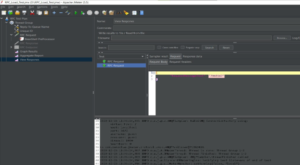
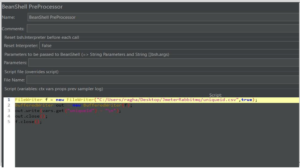

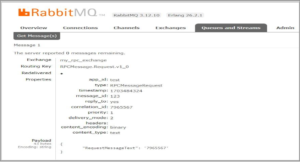
Important link for RabbitMQ:
https://github.com/jlavallee/JMeter-Rabbit-AMQP/blob/master/examples/RPC_Load_Test.jmx
https://github.com/aliesbelik/jmeter-amqp-plugin/releases/tag/v0.3.0
https://www.rabbitmq.com/install-windows.html
https://jatinanejablog.blogspot.com/2016/06/configure-jmeter-to-load-test-rabbit-mq.html





Leave feedback about this